10 Inspiring Contemporary Home Exteriors to Define 2026
Contemporary home exteriors are more than just a first impression; they are a statement of purpose, a blend of materials science, and a direct reflection of modern living. This is not simply a gallery of beautiful houses. It's a strategic deconstruction of the principles that define today's most compelling residential facades. We move beyond surface-level aesthetics to provide a tactical guide for architects, designers, and real estate professionals.
Our analysis dissects 10 distinct approaches to contemporary exterior design, from minimalist purity and industrial chic to sustainable green facades and warm, natural wood applications. Each example is broken down into its core components: materials, form, lighting, and strategic intent. We identify the specific choices that create a cohesive and powerful architectural statement.
More importantly, this guide provides actionable takeaways you can apply directly to your projects. For each style, you will find:
- Key Feature Analysis: A breakdown of materials, rooflines, and fenestration.
- Strategic Insights: The "why" behind the design choices.
- Actionable Prompts: Specific language for generating precise, photorealistic renders with AI tools.
Whether you're presenting concepts to a client, developing marketing materials, or refining your own design language, this curated list will equip you with the insights needed to create and communicate sophisticated contemporary home exteriors. We aim to bridge the gap between inspiration and execution, showing you not just what to build, but how to visualize it with precision and clarity.
1. Minimalist Modern Facades
Minimalist modern facades represent the pinnacle of "less is more" in contemporary home exteriors. This design philosophy champions simplicity and function, stripping away all non-essential ornamentation to emphasize clean lines, geometric forms, and uncluttered surfaces. The result is a sophisticated and timeless aesthetic where high-quality materials and precise construction speak for themselves. This approach creates a powerful visual statement through restraint, focusing on open sightlines and a harmonious connection between the structure and its natural surroundings.
This style, popularized by pioneers like Richard Neutra and Tadao Ando, relies heavily on a neutral color palette. Shades of white, gray, black, and beige dominate, allowing the textures of materials like smooth concrete, glass, steel, and natural wood to provide depth and interest. Understanding your personal design preferences is key to achieving this look; you can discover your house design style to see if minimalism aligns with your vision.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy behind minimalist facades is material honesty and structural clarity. Instead of hiding construction elements, this style celebrates them. A flat roofline isn't just a covering; it's a strong horizontal plane that defines the home's silhouette against the sky. Large, frameless glass panels are not just windows; they are intentional voids that blur the line between indoor and outdoor living spaces.
The success of a minimalist exterior lies in its precision. Every joint, surface, and shadow line is meticulously planned and executed, as there is no decorative trim to hide imperfections.
Actionable Takeaways
To replicate this aesthetic, focus on a curated material palette and leveraging technology for visualization.
- Material Selection: Limit your choices to 2-3 primary materials. Consider board-formed concrete for texture, large-format porcelain tiles for a seamless finish, and vertical cedar or Accoya wood siding for warmth.
- Fenestration: Prioritize large, fixed-pane windows and minimal-profile sliding glass walls. Group windows to create unified geometric compositions rather than scattering them across the facade.
- Visualize with AI: Use a rendering tool like MoldaSpace to test material combinations instantly. Generate variations showing a matte concrete finish versus a smooth stucco, or see how different wood stains interact with a dark metal trim.
- Lighting and Shadow: Model lighting scenarios at different times of the day. A key feature of minimalist contemporary home exteriors is how the sharp lines cast dramatic, changing shadows, adding dynamic character to the simple forms.
2. Industrial Chic with Exposed Materials
Industrial chic exteriors celebrate the raw, unfinished beauty of utilitarian materials, transforming them into a sophisticated residential aesthetic. This style draws inspiration from warehouses, factories, and urban lofts, emphasizing structural honesty by exposing elements like steel beams, raw concrete, and reclaimed brick. The result is a robust and character-rich design that merges historical grit with modern refinement, creating dynamic contemporary home exteriors popular in both urban infill projects and standalone new builds.
This approach, seen in iconic Tribeca loft conversions and modern projects by firms like Shim-Sutcliffe Architects, finds elegance in imperfection. It’s a design language that values texture, patina, and the story materials tell over time. The combination of hard, raw surfaces with expansive glass and clean lines produces a powerful contrast that is both commanding and livable, grounding the home with a sense of history and permanence.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy is aesthetic authenticity through structural expression. Instead of concealing the building's skeleton, this design puts it on full display. A steel I-beam is not just support; it's a primary visual element. A board-formed concrete wall is not just structure; it’s a textured, artistic surface. This style intentionally highlights the joints, bolts, and welds that hold the home together.
The success of an industrial exterior depends on balancing raw, rugged materials with refined, modern details. The contrast between weathered brick and a crisp, black-framed window system is what elevates the design from purely utilitarian to intentionally chic.
Actionable Takeaways
To achieve an industrial chic look, focus on a palette of authentic materials and use visualization tools to perfect the balance between raw and refined elements.
- Material Selection: Combine 2-3 core industrial materials. Consider Corten steel for its evolving patina, reclaimed brick for historical texture, and smooth-finished concrete panels for a modern counterpoint.
- Fenestration: Use large, factory-style windows with dark metal mullions (often steel or aluminum) arranged in grid patterns. These windows flood interiors with light and break up the visual weight of heavy materials.
- Visualize with AI: Use a rendering tool like MoldaSpace to simulate the aging process of materials. Generate variations showing the difference between new Corten steel and its weathered, rust-colored state, or contrast a matte metal roof with glossy window frames.
- Lighting and Softening: Create evening renderings to see how strategic uplighting can highlight the textures of brick and concrete. Use the tool to model how soft landscaping, like ornamental grasses or climbing vines, can soften the hard edges of industrial contemporary home exteriors.
3. Glass and Steel Pavilions
Glass and steel pavilions are the ultimate expression of transparency and structural lightness in contemporary home exteriors. This architectural style uses expansive, high-performance glazing supported by a slender steel framework to dissolve the boundaries between the interior and the surrounding landscape. The design creates an effect of a home that floats in nature, maximizing natural light and transforming the structure into a vitrine that showcases its interior and occupants.
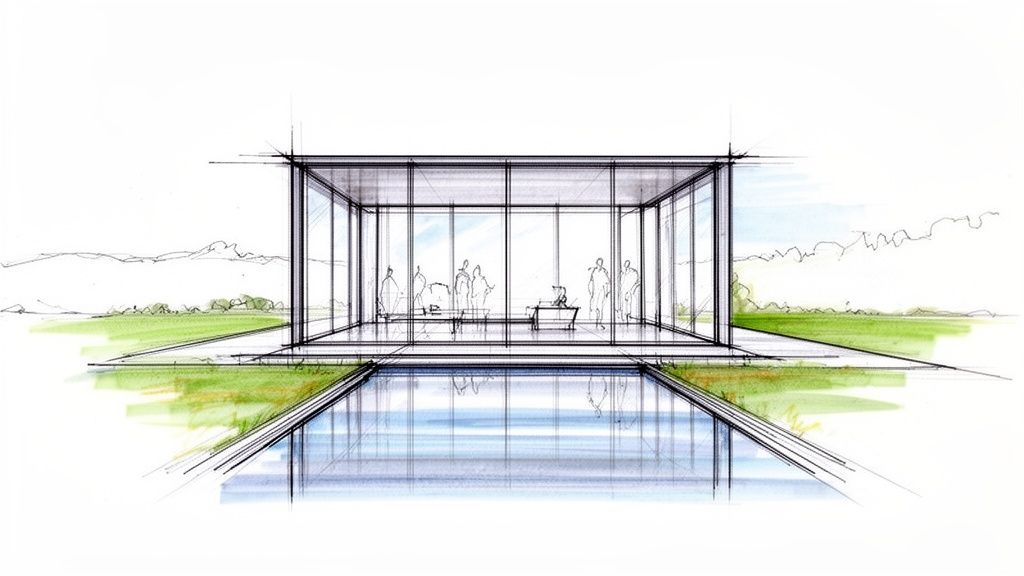
Pioneered by visionaries like Ludwig Mies van der Rohe with his iconic Farnsworth House, this approach prioritizes a seamless visual flow. Modern interpretations, seen in Silicon Valley estates and Swiss hillside villas, push the concept further with advanced glazing technology. The structure itself becomes a minimalist sculpture, where the "walls" are ever-changing views of the outdoors, making it one of the most immersive contemporary home exteriors.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy is dematerialization, where the physical barriers of the home are made to feel as insubstantial as possible. The steel frame provides the necessary structural support but is reduced to its most minimal expression: a clean, elegant grid. The glass is not merely an infill but the primary element of the facade, responsible for defining space, light, and experience.
In a glass pavilion, the exterior is not a facade but a frame. The landscape becomes the "wallpaper," and the home's character shifts dramatically from day to night.
Actionable Takeaways
To achieve this look, the focus must be on the interplay between structure, glass, and light, which can be perfected through visualization.
- Structural Expression: Keep the steel frame elegant and honest. Use thin-profile I-beams or box sections and express the connections clearly. Paint the steel in a dark, recessive color like charcoal or black to make it visually recede.
- Glazing Specification: Opt for ultra-clear, low-iron glass for maximum transparency. Consider triple-pane units for thermal performance and strategically use reflective or tinted coatings to manage solar gain and privacy without sacrificing the view.
- Visualize Transparency with AI: Use a tool like MoldaSpace to generate day and night renderings. Model how interior lighting makes the house glow like a lantern after dark. Test how different interior design schemes and furniture layouts appear from the outside.
- Frame the Landscape: Generate views from inside the virtual model looking out. Adjust window mullion placement to perfectly frame key landscape features like a mature tree, a distant mountain, or a reflective pool.
4. Mixed-Material Facades
Mixed-material facades are a cornerstone of dynamic contemporary home exteriors, combining diverse textures and colors to create visual interest and depth. This design strategy moves beyond monolithic surfaces, artfully layering materials like natural wood, rugged stone, sleek metal, and smooth plaster. The approach allows for a sophisticated visual rhythm, highlighting architectural features and creating a home that feels both grounded and modern. It offers a powerful way to balance aesthetics with performance, using durable materials where needed while adding warmth and character in other areas.
This trend is prominent in global contemporary design, from Scandinavian homes that pair warm wood with dark metal to Australian residences that contrast weathered timber against cool concrete. The key is to create a composition that feels intentional and harmonious rather than disjointed. By carefully selecting and combining materials, architects can craft a unique facade of a house that tells a rich visual story.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy behind mixed-material facades is textural contrast and material hierarchy. This approach uses the inherent qualities of different materials to define form, function, and visual weight. For instance, a heavy stone base can anchor a home to its landscape, while lighter wood or metal cladding on upper floors can create a sense of levity. This intentional layering guides the eye and breaks down the building's mass into more digestible, engaging components.
The art of a successful mixed-material exterior is not just in the combination, but in the transition. The detailing at the junction where wood meets stone, or metal meets glass, is what elevates the design from a simple collage to a cohesive architectural statement.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively implement this aesthetic, focus on creating a balanced composition and using digital tools to perfect the details.
- Material Selection: Choose a primary material to cover 60-70% of the facade and 1-2 accent materials for the remainder. Consider combinations like vertical cedar siding with dark standing-seam metal panels and a board-formed concrete base.
- Create a Hierarchy: Use heavier, more textured materials like stone or brick for the ground floor or foundational elements. Reserve lighter materials like wood or smooth stucco for upper levels or cantilevered sections to enhance architectural forms.
- Visualize with AI: Use a rendering tool like MoldaSpace to rapidly test material combinations. Generate variations showing different proportions, such as a 60/40 wood-to-stone split versus a 30/70 split, to find the optimal balance for your design.
- Detail the Transitions: Model close-up views to perfect the joints between materials. Explore how a recessed channel between wood and plaster creates a clean shadow line, or how a crisp metal edge cap can neatly terminate a stone veneer wall.
5. Sustainable and Green Facades
Sustainable and green facades are a defining feature of forward-thinking contemporary home exteriors, transforming environmental responsibility from a hidden feature into a core aesthetic element. This approach integrates living systems and eco-conscious materials directly into the building's envelope. Features like vertical gardens, green roofs, integrated solar panels, and sustainably sourced wood cladding are not just add-ons; they are fundamental to the architectural identity. The result is a home that breathes, actively contributes to its ecosystem, and makes a powerful statement about conscious living.
This movement, popularized by architects like Stefano Boeri with his iconic Bosco Verticale, treats buildings as living organisms. The design not only minimizes environmental impact but also enhances biodiversity, improves air quality, and provides natural insulation. It merges high-tech solutions with biophilic design principles to create structures that are both visually stunning and ecologically restorative, a key consideration for modern luxury and mainstream markets alike.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy behind a sustainable facade is ecological integration and performance-driven aesthetics. The design visibly showcases its environmental function. A green wall is not merely decoration; it's a living system that cools the building, filters air, and manages stormwater. Solar panels are not awkwardly placed but are seamlessly integrated into the roofline or facade, becoming a deliberate geometric pattern.
The success of a green exterior is measured by its vitality and seamlessness. The design must support the life of its biological components while ensuring the building's technical performance and longevity.
Actionable Takeaways
To create a compelling sustainable facade, focus on integrating living systems and visualizing their evolution over time.
- Material Selection: Prioritize materials with strong green credentials. Use FSC-certified timber like Accoya or Kebony for cladding, recycled steel for structural elements, and locally sourced stone.
- Living Systems: Incorporate a vertical garden or green roof system. Select native plant species that are adapted to the local climate to minimize maintenance and water consumption.
- Visualize with AI: Use a tool like MoldaSpace to model the facade's evolution. Generate renderings that show a green wall at different stages of growth, from initial planting to full maturity. Test how solar panels look with different cladding materials, like dark metal or light wood.
- Seasonal and Lighting Simulation: Create variations showing how the facade changes with the seasons, from lush summer greens to the starker forms of winter. Model day and night scenarios to highlight how integrated lighting can showcase the texture of a living wall after dark.
6. Warm Contemporary with Natural Wood
Warm contemporary design softens the severity often associated with minimalism by introducing the rich, organic texture of natural wood. This approach balances clean lines and modern forms with the inherent warmth of timber, creating an exterior that feels both sophisticated and deeply inviting. By integrating materials like cedar, oak, or thermally modified woods, these contemporary home exteriors establish a strong connection to nature and evoke a sense of calm and comfort, moving away from a purely sterile aesthetic.
This style finds its roots in Scandinavian and Japanese design philosophies, often blending them into a "Japandi" look that values simplicity, craftsmanship, and natural materials. It's a response to the desire for homes that are not just visually striking but also emotionally resonant. The wood can be used as primary cladding, a strategic accent on soffits and entryways, or as delicate screening elements that play with light and shadow, adding layers of visual interest.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy here is tactile contrast and emotional connection. Wood is introduced not just for its color but for its grain, texture, and ability to age gracefully. It serves as a natural counterpoint to colder materials like concrete, steel, and glass, creating a balanced and harmonious composition. The warmth of the timber softens the hard geometry of modern architecture, making the home feel more accessible and human-scaled.
The success of a warm contemporary exterior lies in the thoughtful integration of wood, where it highlights architectural features and enhances the home's relationship with its landscape.
Actionable Takeaways
To achieve this aesthetic, focus on the species of wood and how it interacts with other materials and light.
- Material Selection: Choose woods known for their durability and beauty, such as Western Red Cedar, Ipe, or Accoya. Pair them with contrasting materials like dark metal siding, smooth white stucco, or large-format charcoal panels to make the wood's warmth stand out.
- Application: Use wood to define specific volumes. Consider a vertical rainscreen application for a modern look, or use it to wrap a prominent architectural element like a covered porch or a cantilevered second story.
- Visualize with AI: Use a tool like MoldaSpace to experiment with different wood species and finishes. Generate renderings that show how a light ash versus a rich walnut changes the entire mood of the facade. Test stains and see how the wood will appear when weathered over time.
- Lighting and Grain: Model how natural sunlight interacts with the wood grain at different times of the day. A key feature of these contemporary home exteriors is how light can bring the wood's texture to life, adding a dynamic, natural element to the design.
7. Geometric and Angular Forms
Geometric and angular forms push the boundaries of conventional residential design, treating the home's exterior as a sculptural masterpiece. This approach uses bold, asymmetric lines, dramatic cantilevers, and faceted volumes to create a sense of movement and visual tension. Instead of relying on traditional rectangular shapes, these contemporary home exteriors embrace unexpected angles and dynamic proportions, resulting in structures that are both habitable spaces and works of art.
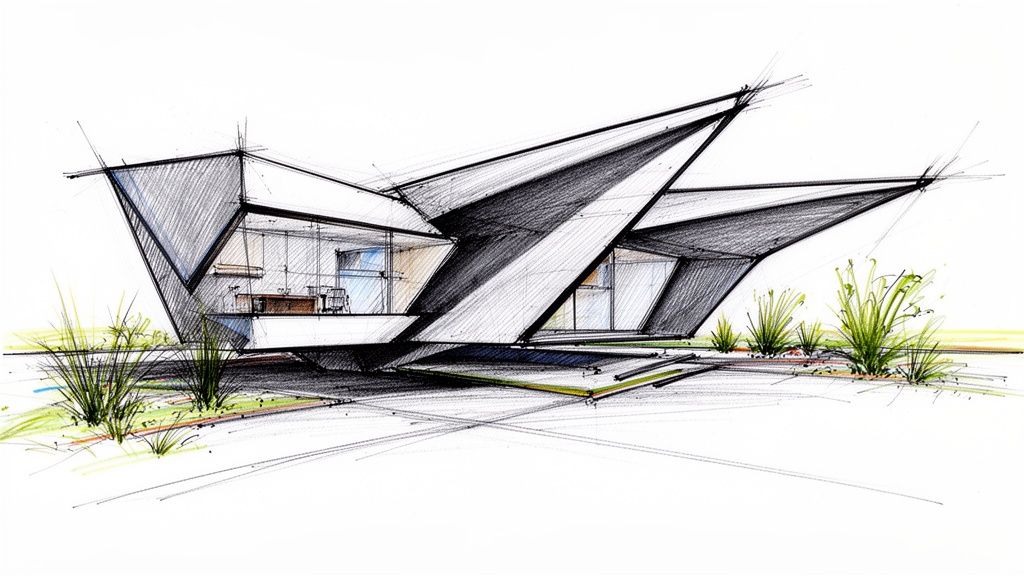

This avant-garde style, heavily influenced by the work of deconstructivist architects like Zaha Hadid and Daniel Libeskind, challenges the viewer's perception of space. Materials such as metal paneling, glass, and concrete are often used to define the sharp planes and create a cohesive, modern aesthetic. Understanding how these forms are perceived from different viewpoints is crucial; you can master this by studying the principles of house perspective drawing to better visualize complex designs.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy is to create architectural drama through volumetric composition. This isn't just about adding an angled roof; it's about composing the entire building mass with interlocking, clashing, or intersecting geometric volumes. Cantilevered sections that appear to defy gravity, sharply angled window recesses, and faceted walls all work together to create a dynamic and memorable silhouette.
The power of a geometric exterior comes from its controlled complexity. Each angle and plane is deliberately placed to interact with light, cast dramatic shadows, and guide the eye around the structure.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively design with geometric forms, focus on composition, material contrast, and advanced visualization.
- Define Dominant Forms: Start with a primary geometric volume and then add intersecting or subtractive elements. For example, a crisp rectangular base can be pierced by a triangular, zinc-clad upper story.
- Material Cohesion: Use materials to emphasize the geometry. Apply a single material, like black standing-seam metal, to an entire angular volume to make it read as one sculptural object.
- Visualize in 3D: Use a tool like MoldaSpace to explore the design from every conceivable angle. Generate aerial perspectives to understand the roofscape's geometric composition and create 360-degree variations to see how the forms interact.
- Model Light and Shadow: Generate renders at sunrise, midday, and sunset. This will reveal how the sharp angles create an ever-changing pattern of light and shadow, which is a key expressive element of this style.
8. Horizontal Lines and Ribbon Windows
Emphasizing strong horizontal lines is a hallmark of many iconic contemporary home exteriors, creating a sense of grounded stability and expansive connection to the landscape. This design principle uses extended roof overhangs, linear material patterns, and, most notably, continuous ribbon windows to draw the eye outward. Inspired by the Prairie School designs of Frank Lloyd Wright and the sleek mid-century modernism of Richard Neutra, this approach feels both classic and distinctly current.
This style is particularly effective in settings with panoramic views, like mountainsides or open prairies, where the ribbon windows can frame the scenery like a cinematic wide-shot. The horizontal elements work to anchor the structure to its site, making it feel like a natural extension of the terrain rather than an object placed upon it. The resulting aesthetic is one of sophisticated calm, where the architecture directs attention to the beauty of its surroundings.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy here is directing the gaze and framing the view. Unlike punched window openings that offer discrete glimpses, ribbon windows create an uninterrupted panoramic experience from the interior. This continuous glazing breaks down the vertical mass of a wall, making the structure feel lighter and more transparent, while the strong horizontal lines of the roof and siding keep it firmly rooted.
The power of this design lies in its ability to create a seamless visual flow. The home doesn't just sit in the landscape; it actively engages with it by controlling and curating the perspective.
Actionable Takeaways
To implement this aesthetic, focus on architectural composition and the interplay between solid and void.
- Material Banding: Use contrasting horizontal siding materials to reinforce the linear effect. Combine smooth stucco bands with thin, horizontal wood slats or dark metal panels to create visual stratification.
- Roof and Overhangs: Design flat or low-pitch roofs with deep, cantilevered overhangs. These not only protect the ribbon windows from direct sun but also cast long, dramatic shadows that accentuate the home's horizontal form.
- Visualize the View: Use a tool like MoldaSpace to precisely model how ribbon windows will frame specific landscape features from key interior viewpoints. Generate renderings that show the changing light and seasonal views through the windows.
- Lighting Design: Plan exterior lighting to uplight the underside of overhangs and graze horizontal siding textures. This technique highlights the linear composition and makes the home a dramatic feature after dark.
9. Textured and Layered Exteriors
Textured and layered exteriors introduce visual and tactile complexity to contemporary design, moving beyond flat surfaces to create facades with depth and character. This approach uses dimensional cladding systems, relief patterns, and overlapping panels to generate intricate shadow lines and a rich, gallery-like aesthetic. It maintains the clean lines of modernism but adds a layer of sophistication, appealing to those who desire a home that feels both current and artistically detailed.
This style, often seen in contemporary Japanese and Swiss architecture, focuses on how materials interact with light. Instead of a single monolithic surface, the facade becomes a dynamic canvas where shadows shift throughout the day, highlighting different textures and creating a sense of movement. It transforms the home's exterior into a deliberate, sculptural composition.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy here is creating depth through material interplay. This approach treats the facade not as a simple barrier but as a multi-layered assembly. Each layer, whether a rainscreen, a decorative slat system, or textured panels, is designed to contribute to the overall composition through its unique finish, form, and shadow-casting properties.
The success of a textured exterior is determined by its rhythm and relief. The design must balance the complexity of the layers with the overall clarity of the home's form, ensuring the details enhance rather than overwhelm the architecture.
Actionable Takeaways
To achieve this sophisticated look, focus on the interplay of materials and use digital tools to perfect the composition.
- Material Selection: Combine materials with contrasting textures. Consider pairing smooth, large-format fiber cement panels with the fine lines of vertical black-stained timber battens or a dimensional, fluted metal cladding.
- Layering Technique: Design with a clear hierarchy. Use a recessed base layer of a dark, smooth material to make the outer, more textured layer appear to float. Overlap panels or create reveals between them to generate crisp shadow lines.
- Visualize with AI: Use a rendering tool to model the facade under different lighting conditions. Generate variations showing how direct morning sun versus soft afternoon light changes the appearance and emphasizes the texture.
- Detailing: Create close-up renderings to study how different materials join. Test variations in the depth and spacing of battens or panels, as a change of even half an inch can dramatically alter the facade's rhythm and shadow patterns.
10. Courtyard and Inward-Facing Contemporary
The inward-facing contemporary home flips the traditional residential model by prioritizing private, curated outdoor spaces over a dominant street-facing presence. This design orients the home around a central courtyard, atrium, or internal garden, creating an intimate and secure connection to nature. Inspired by Mediterranean villas and contemporary Japanese residences, this approach is ideal for urban lots or properties where privacy is paramount, framing nature as a core part of the daily living experience.
This architectural strategy allows for expansive glass walls and seamless indoor-outdoor flow without compromising security or solitude. The street-facing facade is often intentionally understated and solid, contrasting sharply with the light-filled, open interior that engages with the private courtyard. It redefines contemporary home exteriors by making the most personal and tranquil views the primary focus of the design.
Strategic Analysis
The core strategy is creating a private micro-environment. The home acts as a protective shell, buffering the interior living spaces from public view and noise while opening them up to a controlled, serene landscape. This inward orientation allows for maximum natural light and ventilation to penetrate deep into the floor plan, enhancing the home's comfort and energy efficiency.
The success of an inward-facing design lies in its ability to make the home feel expansive and connected to nature, even on a constrained or overlooked site. The courtyard becomes the home's heart and visual anchor.
Actionable Takeaways
To execute this design, focus on the relationship between interior views and the central outdoor space. Visualization tools are critical for perfecting this connection.
- Material Continuity: Use the same or complementary flooring materials from the interior living spaces out into the courtyard to create a seamless transition. This visually extends the room and blurs the indoor-outdoor boundary.
- Layered Privacy: The street-facing elevation can use solid forms like board-formed concrete or stone, while the courtyard-facing walls should feature extensive glazing, such as floor-to-ceiling sliding or bifold doors.
- Visualize Key Views with AI: Use a rendering tool to model the experience from inside. Generate views from the kitchen, living room, and primary bedroom looking into the courtyard to ensure the landscaping and architectural elements create the desired atmosphere.
- Model Light and Ambiance: Generate lighting scenarios showing evening ambiance in the protected courtyard. Test different uplighting on trees, subtle path lighting, and the warm glow from the interior to see how they combine to create a tranquil, resort-like feel.
10 Contemporary Home Exterior Styles Compared
| Style | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimalist Modern Facades | Moderate 🔄 — precise detailing, simple geometry | High ⚡ — premium materials, high-performance glazing | High ⭐ — timeless, photogenic, strong market appeal 📊 | Luxury homes, marketing visuals, clean-site contexts | Clean aesthetic, low maintenance, strong resale ⭐ |
| Industrial Chic with Exposed Materials | High 🔄 — structural coordination, retrofit complexity | Medium–High ⚡ — authentic materials, structural work | High ⭐ — distinctive, characterful, urban appeal 📊 | Loft conversions, urban infill, mixed-use projects | Authentic character, flexible open spaces, photogenic ⭐ |
| Glass and Steel Pavilions | Very High 🔄 — complex glazing & structural systems | Very High ⚡ — costly glazing, HVAC and thermal control | Very High ⭐ — dramatic transparency, premium presentation 📊 | Scenic sites, luxury estates, showroom homes | Maximizes light/visibility, interior as exterior showcase ⭐ |
| Mixed-Material Facades | High 🔄 — careful detailing and transitions | High ⚡ — multiple finishing trades and materials | High ⭐ — dynamic, memorable facades with texture 📊 | Upscale residential developments, bespoke homes | Visual storytelling, material optimization, flexible aesthetics ⭐ |
| Sustainable and Green Facades | High 🔄 — systems integration and specialist design | High upfront ⚡ — green systems, ongoing maintenance | High ⭐ — improved performance, market value uplift 📊 | Green-certified projects, eco-conscious buyers | Energy savings, biophilic appeal, certification-ready ⭐ |
| Warm Contemporary with Natural Wood | Moderate 🔄 — detailing for durability and finishes | Medium–High ⚡ — quality timber and protective treatments | High ⭐ — inviting, broadly appealing aesthetic 📊 | Family homes, wellness-focused and residential settings | Emotional warmth, broad buyer appeal, timeless warmth ⭐ |
| Geometric and Angular Forms | Very High 🔄 — complex geometry, structural engineering | Very High ⚡ — custom fabrication, high construction cost | Very High ⭐ — iconic, highly memorable, luxury impact 📊 | Signature architect homes, marketing showpieces | Distinctive identity, strong social-media/PR appeal ⭐ |
| Horizontal Lines and Ribbon Windows | Moderate–High 🔄 — long spans, custom window systems | High ⚡ — continuous glazing, structural overhangs | High ⭐ — expansive, elegant connection to landscape 📊 | Sites with panoramic views, mid-century reinterpretations | Strong sightlines, timeless composition, landscape framing ⭐ |
| Textured and Layered Exteriors | High 🔄 — precise layering, waterproofing detail | High ⚡ — specialized cladding systems and labor | High ⭐ — rich depth, dynamic shadowing, gallery feel 📊 | Design-forward residences, architectural showcases | Visual richness, hides wear, high perceived value ⭐ |
| Courtyard and Inward-Facing Contemporary | Moderate 🔄 — complex site planning and access | Medium ⚡ — landscaping, water features, larger lots | High ⭐ — private outdoor rooms, strong biophilic feel 📊 | Urban lots needing privacy, warm-climate residences | Privacy, controlled microclimate, intimate outdoor spaces ⭐ |
From Concept to Client: Turning Inspiration into Reality
Throughout this exploration of contemporary home exteriors, a unifying theme emerges: successful design is a deliberate synthesis of form, material, and environment. We've journeyed through the quiet confidence of minimalist modern facades, the raw honesty of industrial chic, and the light-filled transparency of glass and steel pavilions. Each example, from warm contemporary wood cladding to bold geometric forms, underscores that a powerful exterior is not about adopting a fleeting trend but about executing a clear, strategic vision. The most compelling designs tell a story, whether it's one of sustainable integration with nature or of angular, artistic expression.
The core challenge for architects and designers today is not a lack of inspiration, but the friction in translating that inspiration into a tangible, client-approved reality. The journey from a conceptual sketch to a built form is fraught with potential misinterpretations, costly revisions, and communication gaps. This is where the strategic application of technology becomes a critical advantage, transforming the design process from a linear path into a dynamic, iterative dialogue.
Recapping the Core Strategies
As we've analyzed various contemporary home exteriors, several key principles have consistently proven vital for achieving design excellence. Mastering these concepts is the difference between a project that is merely current and one that is truly timeless.
- Material Honesty: The most successful designs allow materials to speak for themselves. Whether it's the grain of natural cedar, the patina of corten steel, or the texture of board-formed concrete, letting the inherent qualities of a material shine through adds depth and authenticity.
- Contextual Harmony: Great contemporary design does not exist in a vacuum. It responds to its site, climate, and surroundings. This was evident in the inward-facing courtyard homes designed for privacy and the sustainable facades that prioritize energy efficiency and local materials.
- Strategic Fenestration: Windows are more than just openings; they are compositional elements that frame views, control light, and define the character of a home. From expansive ribbon windows that emphasize horizontality to carefully placed apertures in a minimalist facade, the placement and scale of glazing are paramount.
- Balanced Complexity: The interplay between simple forms and complex textures creates visual interest. A simple geometric structure can be elevated with layered materials, while a complex angular form might be best rendered in a monolithic material to avoid visual clutter. This balance is central to sophisticated contemporary home exteriors.
Bridging the Vision Gap with Advanced Visualization
The greatest hurdle in client communication is often the "vision gap," the space between the architect's mental image and the client's understanding. Traditional mood boards and 2D elevations can only go so far. To secure buy-in and accelerate approvals, clients need to see and feel the final product with photorealistic clarity.
This is precisely where modern visualization tools become indispensable. Imagine iterating on a mixed-material facade concept in real-time. With an AI-powered platform, you can take a single 3D model and instantly generate dozens of high-fidelity variations.
Strategic Takeaway: Leverage AI-driven rendering to de-risk design decisions. Present clients with multiple, fully realized options for materials, lighting, and landscaping in a fraction of the time it would take for traditional rendering. This allows for faster, more confident decision-making and significantly reduces the likelihood of expensive late-stage changes.
By integrating this technology into your workflow, you can move beyond simply describing your vision to truly demonstrating it. Show your client how a warm contemporary wood exterior will look at sunset versus midday, or compare the visual impact of a dark, moody color palette against a light, airy one. This level of immediate, tangible feedback empowers clients, builds trust, and solidifies your role as an expert guide in the design process. The ability to rapidly prototype and visualize ensures that the final built project is a true reflection of the shared vision, as inspiring and impactful as the initial concept.
Ready to close the gap between your ideas and client-ready presentations? Explore how MoldaSpace uses AI to instantly transform your basic models into stunning, photorealistic renders of contemporary home exteriors. Visit MoldaSpace to see how you can accelerate your design workflow and bring your most ambitious visions to life.



